Please Note: This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Excel versions: 97, 2000, 2002, and 2003. If you are using a later version (Excel 2007 or later), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for later versions of Excel, click here: Weighted Averages in a PivotTable.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated September 7, 2024)
This tip applies to Excel 97, 2000, 2002, and 2003
A good example of how to use calculated fields is for summarizing data differently than you can normally summarize it with a PivotTable. When you create a PivotTable, you can use several different functions to summarize the data that is displayed. For instance, you can create an average of data in a particular field. What if you want to create a weighted average, however? Excel doesn't provide a function that automatically allows you to do this.
When you have special needs for summations—like weighted averages—the easiest way to achieve your goal is to add an additional column in the source data as an intermediate calculation, and then add a calculated field to the actual PivotTable.
For example, you could add a "WeightedValue" column to your source data. The formula in the column should multiply the weight times the value to be weighted. This means that if your weight is in column C and your value to be weighted is in column D, your formula in the WeightedValue column would simply be like =C2*D2. This formula will be copied down the entire column for all the rows of the data.
You are now ready to create your PivotTable, which you should do as normal with one exception: you need to create a Calculated Field. Follow these steps:
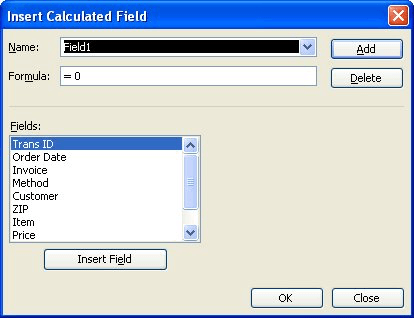
Figure 1. The Insert Calculated Field dialog box.
Your calculated field is now inserted, and you can use the regular summation functions to display a sum of the calculated field; this is your weighted average.
Since there are many different ways that weighted averages can be calculated, it should go without saying that you can modify the formulas and steps presented here to reflect exactly what you need done with your data.
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (2900) applies to Microsoft Excel 97, 2000, 2002, and 2003. You can find a version of this tip for the ribbon interface of Excel (Excel 2007 and later) here: Weighted Averages in a PivotTable.

Create Custom Apps with VBA! Discover how to extend the capabilities of Office 365 applications with VBA programming. Written in clear terms and understandable language, the book includes systematic tutorials and contains both intermediate and advanced content for experienced VB developers. Designed to be comprehensive, the book addresses not just one Office application, but the entire Office suite. Check out Mastering VBA for Microsoft Office 365 today!
Changing the data source PivotTables go to can be a bit tricky. This tip explains what can happen when you re-point your ...
Discover MorePivotTables are used to analyze huge amounts of data. The number of rows used in a PivotTable depends on the type of ...
Discover MoreIf you modify the data on which a PivotTable is based, you'll need to refresh the table so it reflects the modified data. ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
There are currently no comments for this tip. (Be the first to leave your comment—just use the simple form above!)
Got a version of Excel that uses the menu interface (Excel 97, Excel 2000, Excel 2002, or Excel 2003)? This site is for you! If you use a later version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the ribbon interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments